What is the Difference Between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake dives deep into the contrasting worlds of PoW and PoS, shedding light on their distinct characteristics and impact on the crypto landscape. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind these two fundamental concepts in the world of blockchain technology.
From energy efficiency to security and decentralization, this exploration will leave you with a comprehensive understanding of how PoW and PoS shape the future of digital currencies.
Overview of Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS): What Is The Difference Between Proof Of Work And Proof Of Stake
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two consensus algorithms used in blockchain networks to validate transactions and secure the network.
Basic Principles of PoW and PoS
Proof of Work requires network participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. This process consumes a significant amount of computational power and energy.
On the other hand, Proof of Stake validates transactions and creates new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency a participant holds and is willing to “stake” or lock up as collateral. This means that the more cryptocurrency a participant owns, the more likely they are to be chosen to validate transactions.
Validation of Transactions in PoW and PoS, What is the Difference Between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
- In Proof of Work, transactions are validated by miners who compete to solve mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency.
- In Proof of Stake, transactions are validated by participants who hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency and are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake. Participants are rewarded with transaction fees instead of newly minted coins.
Examples of Cryptocurrencies that Use PoW and PoS
- Bitcoin (BTC) is a well-known cryptocurrency that uses Proof of Work to validate transactions and secure the network.
- Ethereum (ETH) is transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake with the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
- Cardano (ADA) is a cryptocurrency that uses Proof of Stake to validate transactions and create new blocks on its blockchain.
Energy Efficiency
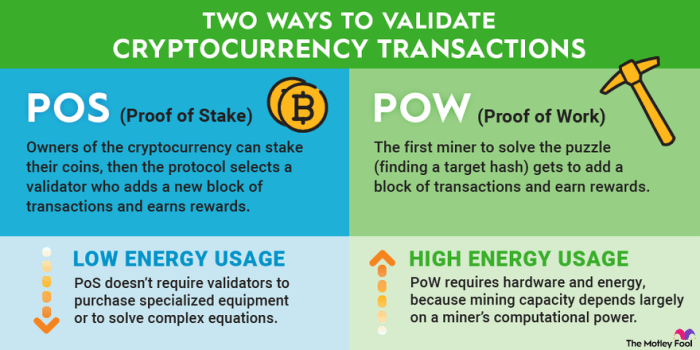
When it comes to energy efficiency, Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) have some major differences that can impact the environment and operational costs.
PoW Energy Consumption
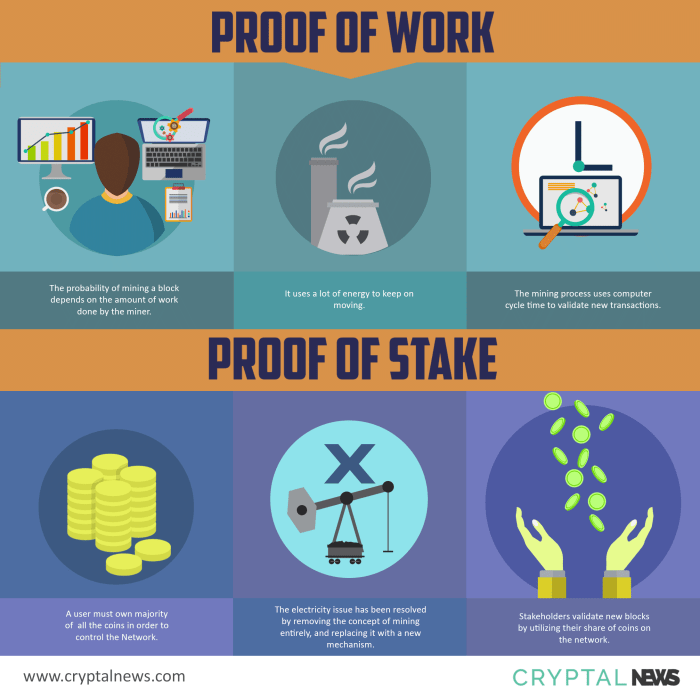
- Proof of Work requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks in the blockchain.
- This process of solving puzzles is extremely energy-intensive and requires powerful hardware and electricity to run 24/7.
- As more miners join the network, the competition for solving puzzles increases, leading to even higher energy consumption.
- Large-scale PoW networks like Bitcoin have been criticized for their massive energy consumption, which is comparable to small countries.
PoS Energy Efficiency
- Proof of Stake, on the other hand, does not require miners to solve complex puzzles or compete for block rewards.
- Instead of miners, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
- This consensus mechanism is much more energy-efficient as it eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining operations.
- Since validators are selected based on their stake in the network, they are incentivized to act honestly to protect their investment.
Security
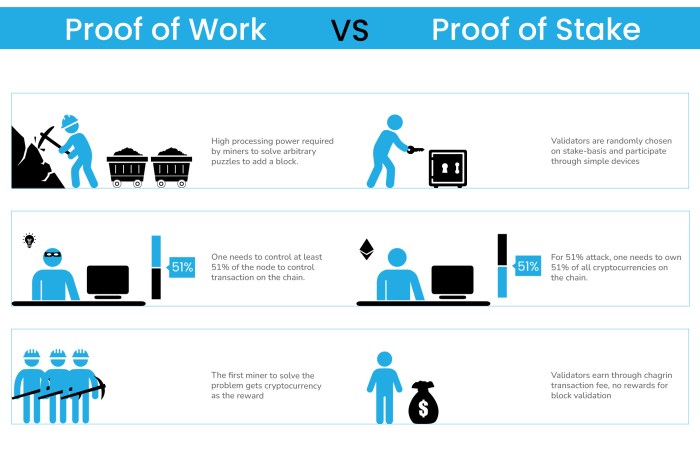
When it comes to the security of a blockchain network, both Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) have their own mechanisms in place to ensure the integrity of the system.
PoW’s security is primarily based on the computational power of miners. In a PoW system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks. The security of the network is maintained by the sheer amount of computational work required to mine a block. This makes it extremely difficult for any single entity to control the network, as they would need to have a majority of the computational power.
On the other hand, PoS uses validators who lock up their coins as collateral to secure the network. Validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they have staked. This means that validators have a financial incentive to act honestly, as they could lose their staked coins if they validate fraudulent transactions. The security of a PoS network is therefore based on the economic incentives of validators rather than computational power.
Comparison of PoW and PoS Security
- In PoW, security is based on computational power of miners, while in PoS, security is based on validators who lock up their coins.
- PoW requires a significant amount of energy to maintain security, while PoS is more energy-efficient.
- Both PoW and PoS have mechanisms in place to prevent attacks and maintain the integrity of the network.
Decentralization
Decentralization is a crucial aspect of blockchain systems, ensuring no single entity has control over the network. Let’s explore how Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) differ in terms of decentralization.
Level of Decentralization in PoW and PoS
In PoW, the network is secured through miners solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. The competitive nature of mining ensures a distributed network of miners, preventing any single entity from gaining control. On the other hand, PoS relies on validators who are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake in the network. This may lead to centralization as wealthier participants have more influence over the network’s operation.

