The Rise of Digital Assets and Their Legal Implications sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Digital assets have taken the world by storm, revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with currency, securities, and unique tokens in the digital realm. As these assets continue to gain prominence, the legal implications surrounding them become increasingly vital to understand and navigate.
Overview of Digital Assets

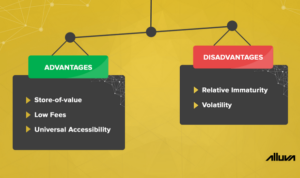
Digital assets are virtual or electronic representations of value that can be owned or traded. They exist in digital form and are stored on digital systems or networks. Examples of digital assets include cryptocurrencies, digital securities, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security. They operate on decentralized technology called blockchain, which enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
Digital Securities
Digital securities are digitally represented financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, or investment contracts. These assets are issued and managed using blockchain technology, providing increased transparency and efficiency in the trading and ownership of securities.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets that represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a specific item or piece of content. They are indivisible and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis like cryptocurrencies. NFTs have gained popularity in the art and collectibles market, as well as in the gaming industry.
Legal Framework for Digital Assets

When it comes to digital assets, understanding the legal frameworks that govern them is crucial. These regulations play a significant role in shaping the landscape of digital assets worldwide.
Cryptocurrencies
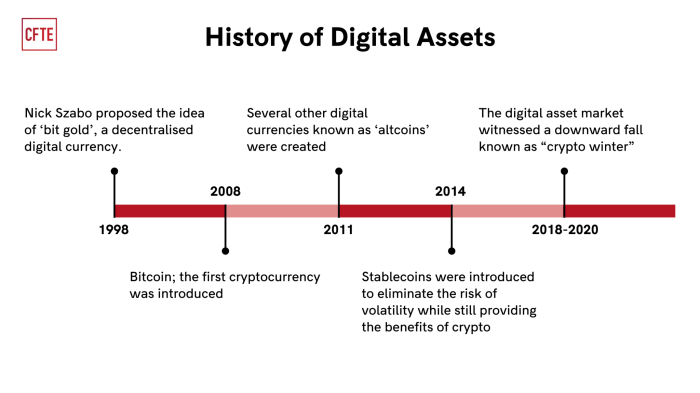
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate in a decentralized manner, which poses challenges for traditional regulatory frameworks. The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies from country to country, with some embracing them as legitimate forms of payment while others restrict or ban their use.
Security Tokens, The Rise of Digital Assets and Their Legal Implications
Security tokens represent ownership of real-world assets and are subject to securities regulations. Issuers of security tokens must comply with strict rules to protect investors and ensure transparency. The legal framework for security tokens aims to prevent fraud and market manipulation.
NFTs
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have gained popularity in the art and collectibles market, presenting unique challenges for regulators. The legal treatment of NFTs varies depending on their use case, with issues surrounding copyright, ownership, and intellectual property rights.
Challenges for Regulators
Regulators face the daunting task of keeping up with the rapid evolution of digital assets. The decentralized nature of many digital assets makes enforcement difficult, leading to concerns about money laundering, tax evasion, and other illicit activities. Balancing innovation and investor protection is key for regulators navigating this complex landscape.
Security and Compliance Issues: The Rise Of Digital Assets And Their Legal Implications
When it comes to digital assets, security and compliance are crucial aspects that cannot be overlooked. The nature of digital assets makes them susceptible to various security risks, and ensuring compliance with regulations is essential to maintain legitimacy in the market.
Security Risks and Mitigation
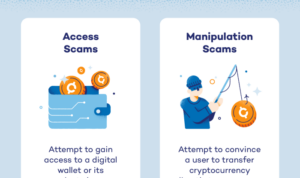
Security risks associated with digital assets include hacking, phishing attacks, and theft due to vulnerabilities in online platforms. To mitigate these risks, investors and companies can implement measures such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, cold storage, and regular security audits.
Importance of Compliance with AML and KYC Regulations
Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations is crucial in the digital asset space to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. By verifying the identity of users and monitoring transactions, companies can ensure a safe and legitimate environment for trading digital assets.
Recent Cases of Fraud or Hacking
- One notable case is the hacking of a major cryptocurrency exchange, resulting in the theft of millions of dollars worth of digital assets. This incident highlighted the importance of robust security measures in the industry.
- Another case involved a fraudulent initial coin offering (ICO) where investors were misled by false promises, leading to legal actions against the individuals responsible for the scam.
- These cases emphasize the need for regulators to enforce strict compliance standards and for market participants to prioritize security to protect investors and maintain trust in the digital asset market.
Smart Contracts and Legal Enforceability
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the terms of the contract when predefined conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries.
Legal Enforceability of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have gained popularity in the digital asset space due to their efficiency and automation. However, the legal enforceability of smart contracts varies across different jurisdictions. While some countries have recognized smart contracts as legally binding, others are still in the process of developing regulations to address their use.
- In the United States, the legal enforceability of smart contracts depends on whether they meet the requirements of traditional contract law, such as offer, acceptance, and consideration. Courts have started to recognize smart contracts as valid agreements, but challenges remain in interpreting and enforcing these contracts.
- In the European Union, the legal status of smart contracts also varies among member states. Some countries have taken steps to provide legal recognition to smart contracts, while others are still evaluating their implications.
- In Asia, countries like Singapore and Japan have been at the forefront of adopting regulations that recognize smart contracts. These jurisdictions have established frameworks to ensure the enforceability of smart contracts and provide clarity on their legal standing.
Challenges in Resolving Disputes related to Smart Contracts
Resolving disputes related to smart contracts poses challenges, especially in the absence of traditional legal frameworks. The automated nature of smart contracts can complicate dispute resolution processes, as parties may face difficulties in interpreting the code and identifying the responsible party in case of breaches.
- One of the main challenges is the lack of established legal precedents for smart contract disputes. Courts may struggle to apply existing laws to these novel contracts, leading to uncertainty and delays in resolving disputes.
- Another challenge is the potential for vulnerabilities in smart contract code, which can be exploited by malicious actors to manipulate the terms of the contract. This raises concerns about the security and integrity of smart contracts, further complicating dispute resolution efforts.
- Furthermore, the cross-border nature of digital asset transactions involving smart contracts can add complexity to dispute resolution, as parties may be subject to different legal jurisdictions and regulations, making it challenging to determine the applicable laws and procedures for resolving disputes.