As Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with american high school hip style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Blockchain technology isn’t just about cryptocurrencies; it’s a revolutionary system that relies on consensus mechanisms to ensure trust and security in a decentralized network. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of blockchain consensus mechanisms to uncover the inner workings of this innovative technology.
Overview of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms: Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain consensus mechanisms are protocols that enable nodes in a decentralized network to agree on the validity of transactions. Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and security of blockchain networks by preventing double-spending and maintaining a single source of truth.
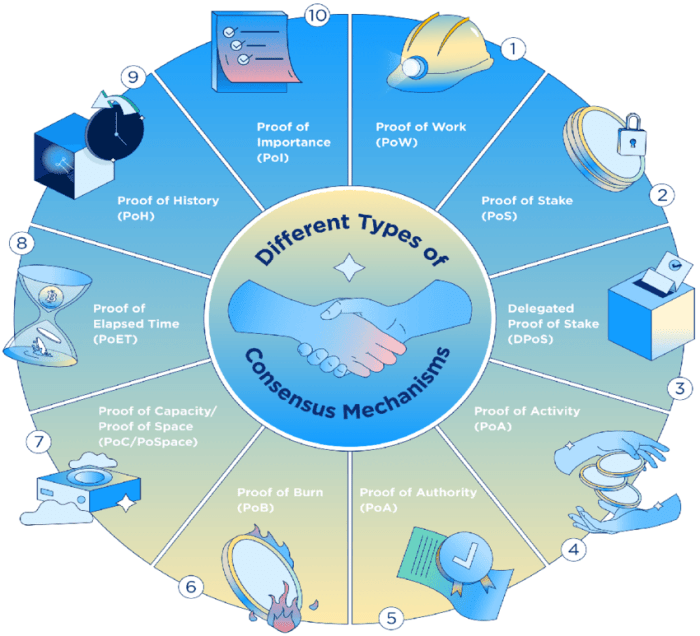
Popular Consensus Mechanisms
- Proof of Work (PoW): Popularized by Bitcoin, PoW requires nodes to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold, rather than computational power.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): DPoS involves a select group of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions on behalf of the network.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): PoA relies on approved validators who have a reputation to maintain, ensuring the network’s security.
Importance of Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are essential for maintaining the decentralized nature of blockchain networks. By establishing trust and agreement among nodes, consensus mechanisms help prevent fraud, censorship, and manipulation of data. Without robust consensus mechanisms, blockchain networks would be vulnerable to attacks and compromise the trust of users.
Proof of Work (PoW) Consensus Mechanism
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks to validate transactions and create new blocks in the chain. It involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to secure the network and achieve consensus among nodes.
How Proof of Work Works
In the Proof of Work mechanism, miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle using their computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle broadcasts the solution to the network for verification. Once verified, the new block is added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency.
Mining and its Relationship to PoW, Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Mining is the process of using computational power to validate transactions and create new blocks in the blockchain. Miners in a PoW system compete to solve puzzles and add blocks to the chain. The difficulty of the puzzles adjusts dynamically to ensure a consistent block creation time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PoW
- Advantages:
- Proven security: PoW has been battle-tested and proven to secure blockchain networks effectively.
- Decentralization: PoW allows anyone with the necessary hardware to participate in securing the network.
- Incentivizes miners: Miners are rewarded for their work, which helps maintain the network’s integrity.
- Disadvantages:
- High energy consumption: PoW requires significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption.
- Centralization of mining power: The need for specialized hardware can lead to centralization of mining power in the hands of a few.
- Susceptibility to 51% attacks: PoW networks are vulnerable to attacks if a single entity controls more than 50% of the network’s computational power.
Proof of Stake (PoS) Consensus Mechanism
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a blockchain consensus mechanism that operates differently from Proof of Work (PoW). In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Role of Validators and Staking in PoS
In the PoS system, validators are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks on the blockchain. These validators are selected based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to lock up as a stake. The more coins a validator stakes, the higher the chance they have of being chosen to create a new block and earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and newly minted coins.
- Validators play a crucial role in securing the network and ensuring the validity of transactions.
- Staking encourages validators to act honestly and in the best interest of the network, as they have a financial stake in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain.
- Validators who attempt to validate fraudulent transactions risk losing their staked coins, providing an incentive for honest behavior.
Staking in PoS incentivizes validators to work for the security and efficiency of the blockchain, as their own assets are on the line.
Environmental Implications of PoS
Unlike PoW, which requires significant computational power and energy consumption to validate transactions, PoS is considered to be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Since PoS does not rely on solving complex mathematical puzzles like PoW, it consumes significantly less power, making it a more sustainable alternative.
- By reducing the need for powerful mining rigs and energy-intensive computations, PoS helps lower the carbon footprint of blockchain networks.
- With PoS, validators are not competing against each other to solve puzzles, leading to a more streamlined and eco-friendly process of reaching consensus.
- The environmental impact of PoS is a major advantage over PoW, especially in the context of increasing concerns about energy consumption and climate change.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Consensus Mechanism
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks to achieve decentralized validation of transactions. In DPoS, token holders vote for a select group of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and securing the network.
How Delegated Proof of Stake Works and its Purpose
In DPoS, token holders elect delegates to validate transactions and create new blocks. These delegates take turns producing blocks and are incentivized to act honestly to maintain their position. The purpose of DPoS is to improve scalability and efficiency compared to other consensus mechanisms like PoS.
- Delegates validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Token holders vote for delegates to represent them in the network.
- Delegates are responsible for securing the network and maintaining consensus.
Key Differences between DPoS and PoS
One key difference between DPoS and PoS is the delegation of block validation tasks to a select group of individuals in DPoS, whereas in PoS, all token holders can participate in block validation. This delegation model in DPoS can lead to faster block generation and lower energy consumption.
- DPoS relies on a select group of delegates for block validation.
- PoS allows all token holders to participate in block validation.
- DPoS aims to improve efficiency and scalability through delegation.
Scalability and Efficiency Aspects of DPoS
DPoS is designed to address scalability issues faced by blockchain networks by streamlining the block validation process. With a limited number of delegates responsible for block production, DPoS can achieve faster transaction processing times and higher throughput compared to PoS.
- DPoS enhances scalability by delegating block validation tasks.
- Efficiency is improved in DPoS due to faster block generation and lower energy consumption.
- Throughput is increased in DPoS networks, leading to improved network performance.